In a world where technology transforms daily life at breakneck speed, preparing children and students for the challenges ahead is more important than ever. STEM education—focusing on Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics—offers a powerful learning approach that builds essential skills for real-world problem solving and career readiness. This article explains what STEM education really means, how it differs from traditional schooling, why it matters so much in today’s economy, and how it benefits learners of all ages.
What Does STEM Education Really Mean?
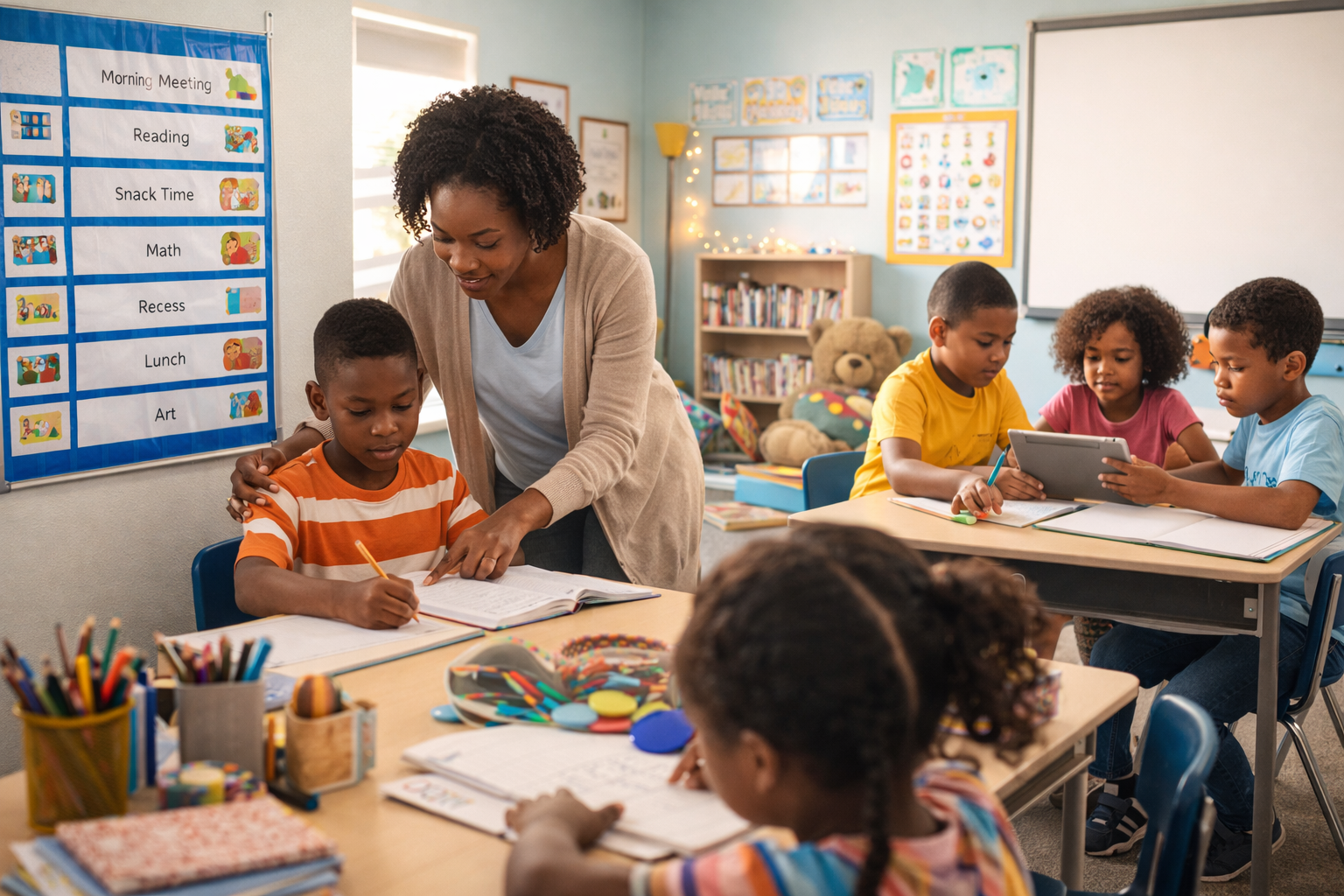
STEM is an educational approach that blends science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into a unified learning experience. Instead of teaching these subjects separately, STEM connects them in ways that mirror how problems are solved outside the classroom.
In practice, STEM encourages students to:
- Investigate real-world problems
- Build solutions through experimentation
- Think critically and creatively
- Collaborate with peers
Rather than memorizing facts, learners engage with meaningful projects that deepen understanding and make knowledge more memorable.
How STEM Learning Differs from Traditional Instruction
Traditional education often focuses on rote learning and memorization within isolated subjects. STEM shifts that model by:
| Traditional Education | STEM Education |
|---|---|
| Lessons taught separately | Subjects integrated |
| Memorization-based | Problem-solving-focused |
| Teacher-centered | Student-centered |
| One “right answer” | Open-ended inquiry |
This structure better reflects how challenges arise and are addressed in real life—from engineering new products to analyzing environmental data.
Key Benefits of STEM Education
1. Builds Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
One of the strongest advantages of STEM learning is its emphasis on thinking deeply and creatively about problems. Rather than simply answering textbook questions, students learn to analyze complex situations, test hypotheses, and refine solutions. These skills serve learners in academic settings and everyday life.
2. Enhances Technological Literacy
In an age where technology plays a role in almost every industry—healthcare, transportation, communications—understanding technology basics is essential. STEM education introduces learners to digital tools, coding concepts, data analysis, and systems thinking that are increasingly valuable in educational and professional contexts.
3. Encourages Collaboration and Communication
STEM activities often involve group work, where students must share ideas, delegate tasks, and explain their thinking. These experiences cultivate teamwork and communication skills that are highly valued in workplaces and communities alike.
4. Boosts Confidence Through Hands-On Learning
When students build, test, fail, and retry—a common cycle in STEM projects—they learn that effort and resilience are more important than perfection. Completing hands-on projects gives learners a sense of accomplishment and encourages a growth mindset.
5. Prepares Students for Future Careers
The global economy increasingly demands workers with STEM-related abilities. Fields like software development, renewable energy, biotechnology, and data science reward individuals who can think analytically, adapt to new technologies, and solve new kinds of problems. Early exposure to STEM equips learners with a foundation for these in-demand roles.
Examples of STEM in Action
Here are a few practical ways STEM learning plays out in real educational settings:
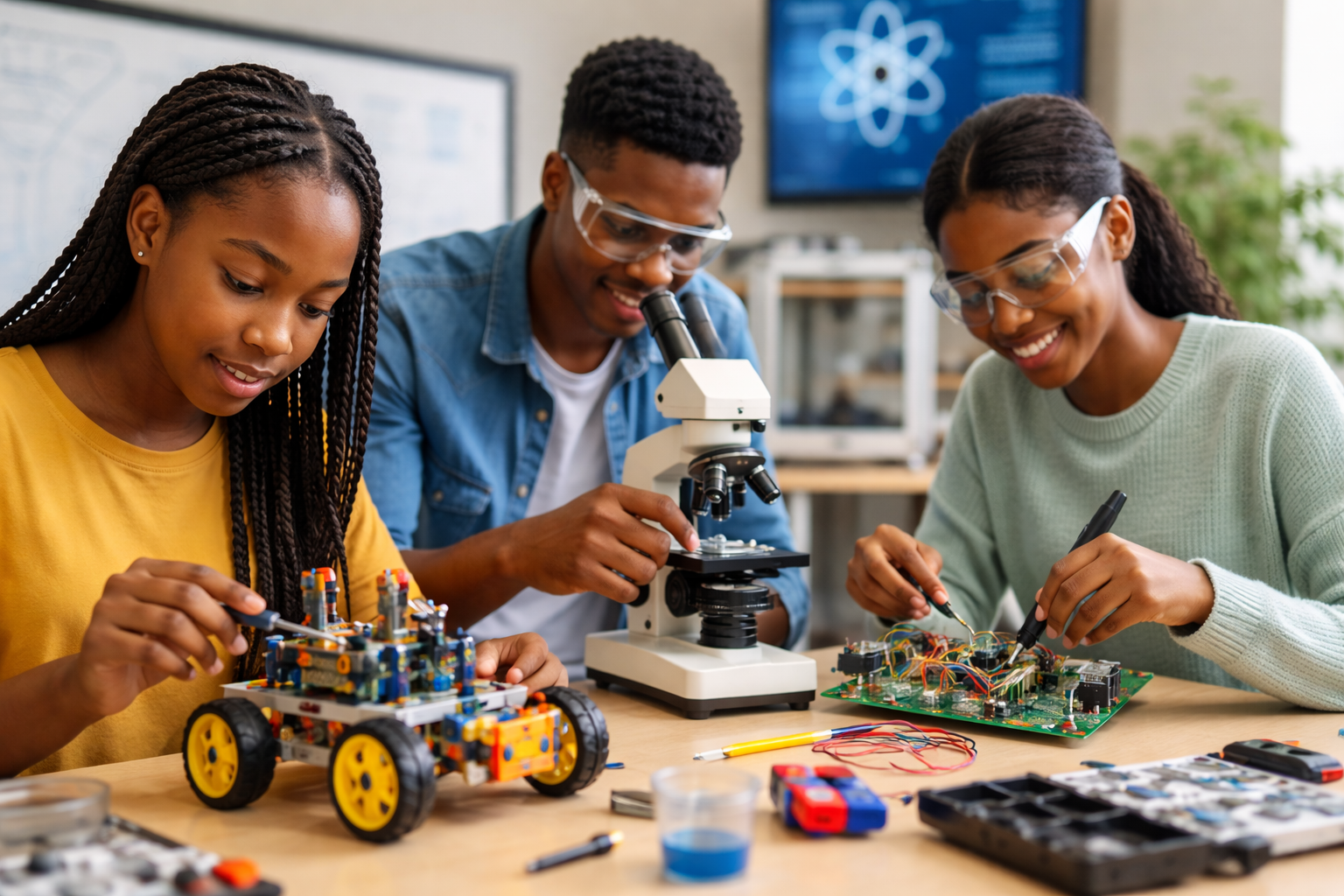
- Robotics and Coding Projects: Students design and program robots, linking engineering principles with computer science logic.
- Environmental Science Experiments: Learners collect and analyze ecological data to understand climate change impacts.
- Engineering Challenges: Teams design prototypes (like water filtration systems or bridges) that must meet specific criteria.
- Data-Driven Math Projects: Math becomes a tool for solving real-world problems such as predicting trends from data sets.
Who Benefits from STEM Education?
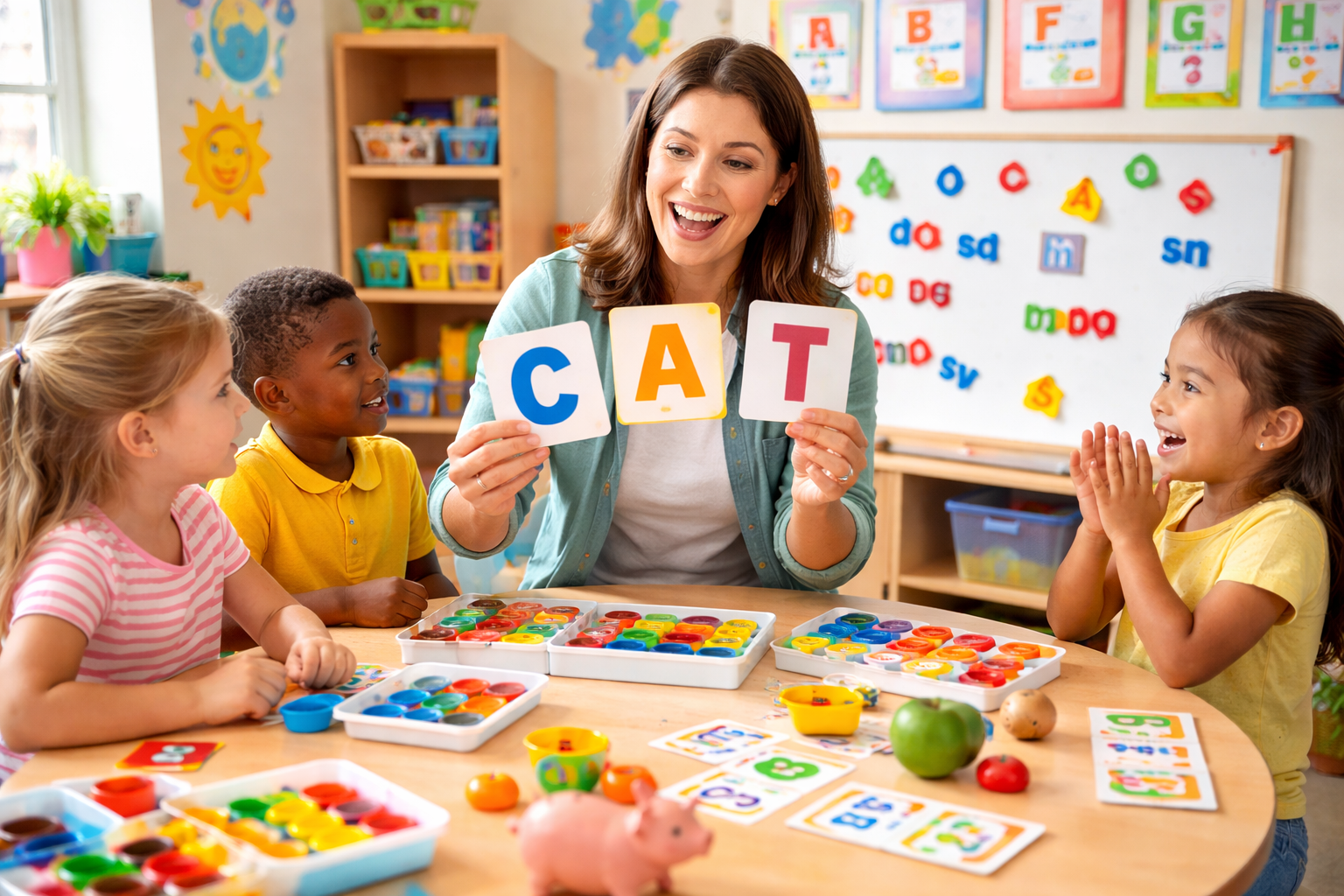
Students of All Ages
From elementary school to university level, STEM education develops skills that benefit learners across subjects and careers. Younger students gain confidence and curiosity, while older learners build specialized knowledge for advanced study and employment.
Teachers and Educators
With hands-on and project-based instruction, teachers can create more engaging lessons that connect classroom concepts to real-world issues, boosting student participation and retention of material.
Communities and Economies
Well-implemented STEM programs contribute to a skilled workforce, fostering innovation and competitiveness. Communities that support STEM learning often see growth in technology sectors and related industries as graduates enter the workforce.
Challenges in Implementing STEM Education
While the benefits are clear, several challenges can hinder STEM education’s success:
- Limited Resources: Not all schools have access to labs, tools, or technology needed for effective STEM programs. (extramarks.com)
- Training Needs: Teachers require ongoing professional development to confidently deliver STEM-rich instruction.
- Equitable Access: Students in underserved or rural communities may have fewer opportunities to engage with advanced STEM experiences.
Addressing these barriers requires investment, policy support, and community engagement.
Expanding STEM Beyond School Walls
STEM learning doesn’t stop when the school bell rings. Lifelong learners can deepen their skills through:
- Online courses and coding bootcamps
- Science fairs and innovation challenges
- Maker spaces and community labs
- STEM clubs and extracurricular competitions
These opportunities help learners stay engaged with evolving technologies and concepts throughout life.
Final Thoughts: A Pathway to Lifelong Learning and Innovation
STEM education represents more than an academic category—it fosters a mindset geared toward curiosity, resilience, and informed experimentation. By integrating science, technology, engineering, and math in meaningful ways, it equips learners with the tools needed to thrive in the complex challenges of the modern world.
Whether your goal is to nurture future engineers, empower critical thinkers, or prepare adaptable global citizens, STEM education lays a foundation for success far beyond the classroom.
Key Concepts Covered: STEM education, interdisciplinary learning, real-world skills, critical thinking, collaboration, technology literacy, career readiness, inclusive education.