Teaching is not a one-size-fits-all activity. Every learner is different, and effective education depends on using teaching approaches that match the subject, the learning environment, and the needs of students. Understanding the different types of teaching can help educators teach more effectively and help learners understand how they learn best.
In this article, we will explore four widely recognized types of teaching used in schools, colleges, and informal learning environments. Each type has its own strengths, challenges, and best-use situations. By the end, you will have a clear, practical understanding of how these teaching types work and why they matter.
What Are the Types of Teaching?
Teaching types refer to structured approaches educators use to deliver knowledge, develop skills, and support understanding. While there are many teaching styles and strategies, most modern educational practices can be grouped into four broad types:
- Lecture-Based Teaching
- Inquiry-Based Teaching
- Collaborative Teaching
- Experiential Teaching
These types are not competing methods. In practice, effective teachers often combine them to create balanced and engaging learning experiences.
1. Lecture-Based Teaching
What Is Lecture-Based Teaching?
Lecture-based teaching is one of the oldest and most traditional forms of instruction. In this approach, the teacher delivers information directly to students, usually through spoken explanation, demonstrations, or presentations. Students listen, take notes, and absorb content that is carefully structured by the teacher.
This method is commonly used in classrooms, universities, seminars, and online courses where large amounts of information need to be communicated efficiently.
Key Characteristics
- Teacher-centered instruction
- Structured lessons with clear objectives
- Emphasis on explanations and factual knowledge
- Limited student interaction during delivery
Practical Examples
- A history teacher explaining major world events
- A university professor presenting scientific theories
- An online instructor delivering a recorded lesson
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths
- Efficient for covering large topics
- Easy to organize and manage
- Useful for introducing new concepts
Limitations
- Passive learning if overused
- Less engagement for some learners
- Limited feedback during instruction
Lecture-based teaching works best when combined with discussion, questions, or follow-up activities that help students apply what they have learned.
2. Inquiry-Based Teaching
What Is Inquiry-Based Teaching?
Inquiry-based teaching encourages learners to ask questions, investigate problems, and discover knowledge through exploration. Instead of giving direct answers, the teacher guides students to think critically and find solutions on their own.
This approach supports curiosity, independent thinking, and deeper understanding of concepts.
Key Characteristics
- Student-centered learning
- Focus on questions and problem-solving
- Teacher acts as a guide or facilitator
- Emphasis on reasoning and evidence
Practical Examples
- Students researching why a scientific phenomenon occurs
- Learners exploring social issues through guided questions
- Classroom discussions driven by student curiosity
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths
- Builds critical thinking skills
- Encourages active participation
- Promotes deeper understanding
Limitations
- Can be time-consuming
- Requires strong guidance from the teacher
- May challenge learners who prefer structure
Inquiry-based teaching is especially effective in subjects like science, social studies, and problem-based learning environments.
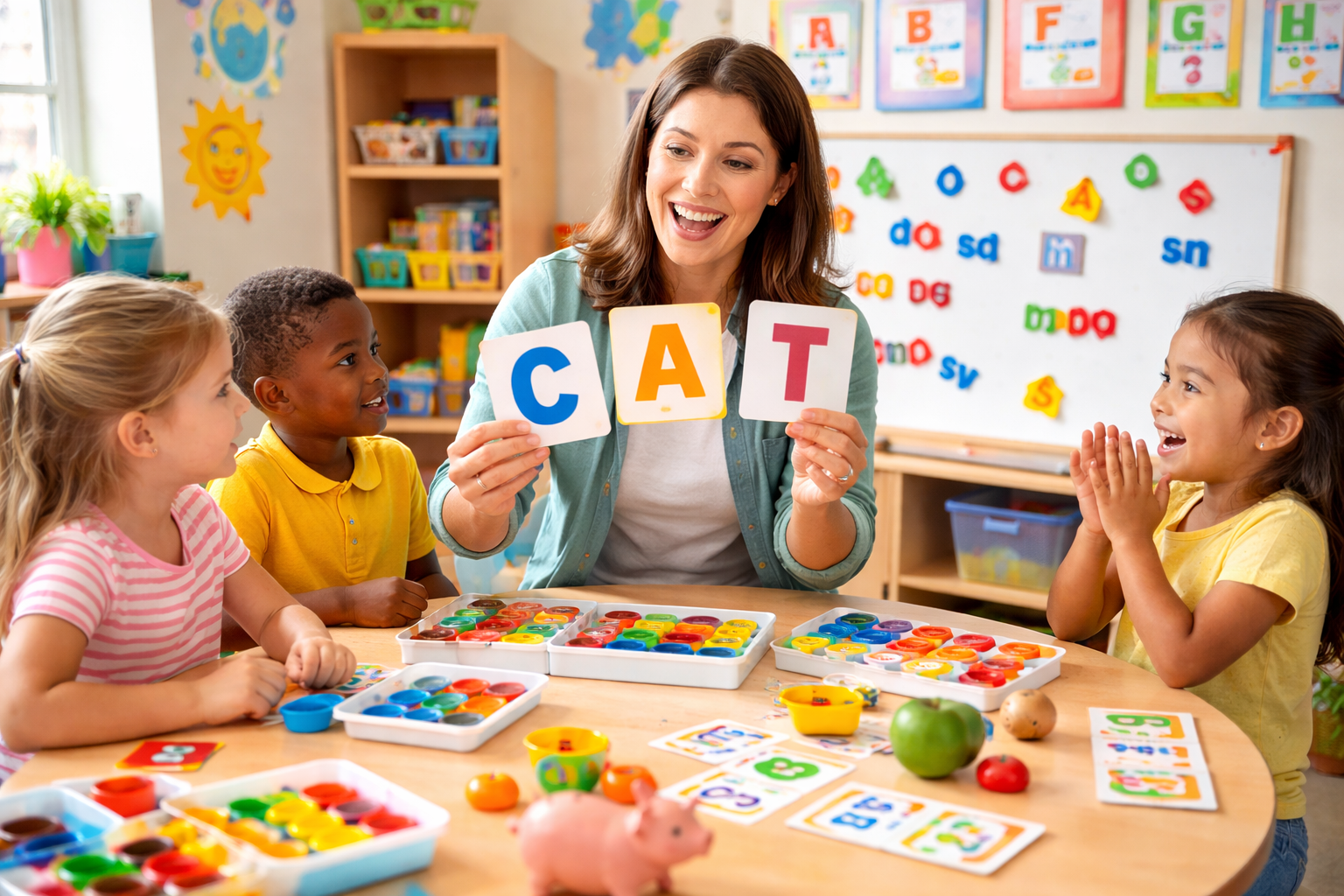
3. Collaborative Teaching
What Is Collaborative Teaching?
Collaborative teaching focuses on learning through interaction with others. Students work together in pairs or groups to solve problems, complete tasks, or discuss ideas. The teacher supports cooperation and ensures that learning goals are met.
This type of teaching reflects real-world situations where teamwork and communication are essential.
Key Characteristics
- Group-based learning activities
- Shared responsibility among students
- Emphasis on communication and teamwork
- Teacher monitors and supports group dynamics
Practical Examples
- Group projects and presentations
- Peer-to-peer discussions
- Classroom debates or role-playing activities
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths
- Develops communication skills
- Encourages diverse perspectives
- Improves social and teamwork abilities
Limitations
- Unequal participation can occur
- Requires clear instructions and structure
- Assessment may be more complex
Collaborative teaching is widely used in modern classrooms and is especially useful for developing interpersonal and problem-solving skills.
4. Experiential Teaching
What Is Experiential Teaching?
Experiential teaching is based on learning through direct experience. Instead of only reading or listening, students actively engage in tasks that help them apply knowledge in real or simulated situations.
This type of teaching connects theory with practice, making learning more meaningful and memorable.
Key Characteristics
- Hands-on learning experiences
- Real-world application of knowledge
- Reflection on actions and outcomes
- Active learner involvement
Practical Examples
- Laboratory experiments
- Field trips and internships
- Simulations, workshops, and practical demonstrations
Strengths and Limitations
Strengths
- Enhances long-term understanding
- Increases learner motivation
- Builds practical skills
Limitations
- Can require more resources
- Needs careful planning
- May not suit all topics equally
Experiential teaching is highly effective in vocational training, science education, and skill-based learning environments.
How These Teaching Types Work Together
Although these four types of teaching are distinct, they are most effective when used together. A single lesson may include:
- A short lecture to introduce a topic
- Inquiry-based questions to spark curiosity
- Group work for collaboration
- Hands-on activities for real-world application
Blending teaching types allows educators to address different learning styles and create a balanced educational experience.
Why Understanding Teaching Types Matters
Understanding the different types of teaching benefits both educators and learners.
For teachers, it helps to:
- Choose the right method for each lesson
- Improve student engagement
- Support diverse learning needs
For learners, it helps to:
- Recognize personal learning preferences
- Become more active participants in education
- Develop a range of skills beyond memorization
Education becomes more effective when teaching methods are chosen intentionally rather than by habit.
Conclusion
The four main types of teaching—lecture-based, inquiry-based, collaborative, and experiential—each play an important role in effective education. No single approach is perfect on its own, but together they create rich and meaningful learning experiences.
By understanding how these teaching types work and when to use them, educators can improve learning outcomes, and students can gain deeper knowledge and practical skills. Whether in a classroom, online environment, or informal setting, thoughtful teaching methods make learning clearer, more engaging, and more effective.