Learning to read is one of the most important skills a person develops in life. It affects academic success, communication, confidence, and lifelong learning. At the heart of strong reading ability lies phonics—a foundational approach that helps readers understand how letters and sounds work together. While phonics is often associated with early childhood education, its impact extends far beyond simply sounding out words. It plays a crucial role in word decoding and reading comprehension at every stage of learning.
This article explains how phonics supports reading development, why it matters for comprehension, and how it helps readers become more confident and independent. Whether you are a parent, educator, or curious reader, understanding phonics can provide valuable insight into how reading skills are built and strengthened.
What Is Phonics?
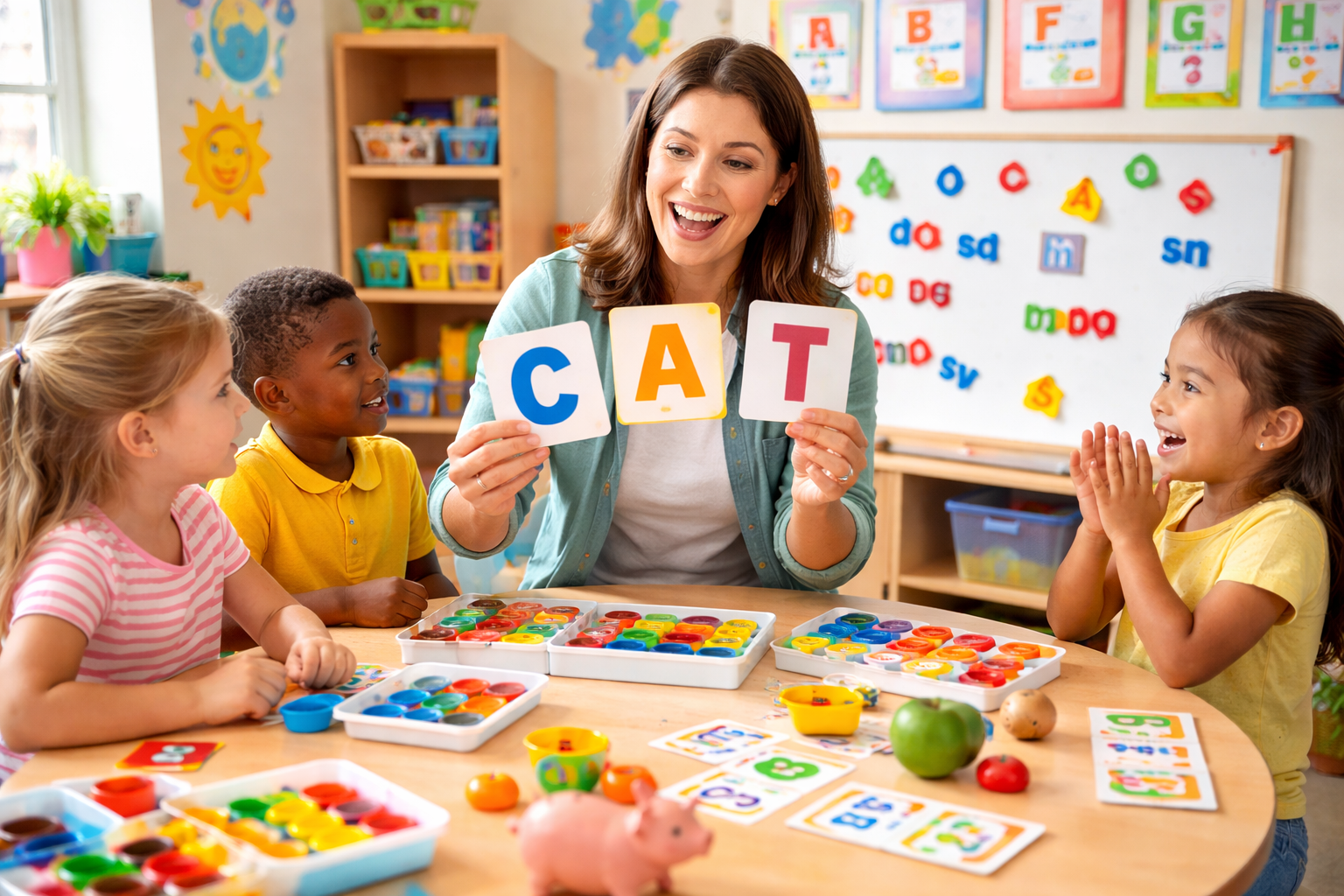
Phonics is a method of teaching reading that focuses on the relationship between letters (graphemes) and the sounds they represent (phonemes). Instead of memorizing whole words by sight alone, learners are taught how to decode words by breaking them into sounds and blending those sounds together.
For example:
- The word cat can be decoded by identifying the sounds /c/ /a/ /t/ and blending them.
- The word ship involves recognizing the digraph sh as a single sound.
Phonics instruction helps readers understand predictable patterns in written language, making reading more logical and less reliant on guesswork.
Understanding Word Decoding
What Is Word Decoding?
Word decoding is the ability to translate written words into spoken language. It involves recognizing letters, understanding their sounds, and blending those sounds to read words accurately.
Effective decoding allows readers to:
- Read unfamiliar words independently
- Improve reading accuracy
- Build confidence while reading new texts
Without decoding skills, readers often struggle to make sense of text, especially as reading materials become more complex.
How Phonics Supports Word Decoding
Phonics provides a clear system for decoding words. Instead of relying on memorization, readers learn rules and patterns they can apply across many words.
Key ways phonics helps with word decoding include:
- Teaching consistent sound-letter relationships
- Helping readers recognize common spelling patterns
- Reducing confusion when encountering new words
- Encouraging problem-solving rather than guessing
As readers practice phonics, decoding becomes faster and more automatic, freeing mental energy for understanding meaning.
The Link Between Phonics and Reading Comprehension
Why Decoding Alone Is Not Enough
Reading comprehension is the ability to understand, interpret, and think critically about text. While decoding is essential, comprehension involves additional skills such as vocabulary knowledge, background understanding, and attention.
However, decoding and comprehension are closely connected. If a reader struggles to decode words, comprehension often suffers because too much effort is spent trying to read individual words.
How Phonics Improves Comprehension
Phonics supports reading comprehension by making word recognition more efficient. When readers can decode words quickly and accurately, they can focus on meaning rather than mechanics.
Phonics helps comprehension by:
- Improving reading fluency
- Supporting vocabulary development
- Allowing smoother sentence-level understanding
- Reducing frustration and cognitive overload
Over time, strong phonics skills contribute to better understanding of longer texts, including stories, informational articles, and academic materials.
Phonics and Reading Fluency
What Is Reading Fluency?
Reading fluency refers to the ability to read with speed, accuracy, and appropriate expression. Fluent readers do not pause excessively to decode words; instead, reading feels natural and rhythmic.
How Phonics Builds Fluency
Phonics instruction helps readers recognize patterns automatically. As decoding becomes quicker, fluency improves.
Benefits of phonics for fluency include:
- Faster word recognition
- Fewer reading interruptions
- Improved confidence and motivation
- Better understanding of sentence structure
Fluency acts as a bridge between decoding and comprehension, making phonics a key contributor to overall reading success.
Phonics and Vocabulary Development
When readers decode words independently, they are exposed to a wider range of vocabulary. Instead of avoiding unfamiliar words, they learn how to approach them with confidence.
Phonics supports vocabulary growth by:
- Encouraging exploration of new words
- Helping readers connect pronunciation with meaning
- Reinforcing spelling and word structure
- Supporting retention of new terms
As vocabulary expands, comprehension improves, creating a positive cycle of reading development.
Benefits of Phonics for Different Learners
Early Readers
For young learners, phonics lays the groundwork for reading success. It provides structure and clarity at a stage when language skills are still developing.
Early benefits include:
- Faster progress in reading
- Reduced reliance on memorization
- Stronger spelling skills
- Increased confidence
Struggling Readers
Phonics is especially helpful for readers who experience difficulty with reading accuracy or comprehension. It offers clear strategies for breaking down words and understanding text.
For struggling readers, phonics can:
- Address gaps in foundational skills
- Reduce reading anxiety
- Improve consistency in reading performance
- Support long-term improvement
Older Learners and Adults
Phonics is not limited to children. Older students and adults who missed early reading instruction can also benefit.
Phonics helps older learners by:
- Rebuilding foundational skills
- Supporting literacy in academic or professional settings
- Improving reading speed and accuracy
- Increasing independence and confidence
Practical Examples of Phonics in Action
To understand how phonics works in real reading situations, consider these examples:
- A reader encounters the word unhappiness and breaks it into meaningful parts: un-happy-ness.
- A child reads the sentence “The frog jumped across the pond” by decoding unfamiliar words rather than skipping them.
- A student recognizes that light, night, and bright share a common spelling pattern, making reading easier.
These everyday moments show how phonics supports both decoding and comprehension in practical ways.
Common Misunderstandings About Phonics
Despite its benefits, phonics is sometimes misunderstood. Clarifying these misconceptions helps highlight its true value.
Phonics Is Not Memorization
Phonics teaches patterns, not lists of words. The goal is understanding, not rote learning.
Phonics Does Not Ignore Meaning
While phonics focuses on sounds, it supports meaning by making word recognition easier and more accurate.
Phonics Is Not a Standalone Skill
Phonics works best alongside other reading strategies, such as comprehension practice, vocabulary building, and discussion.
How Phonics Fits Into a Balanced Reading Approach
Strong reading instruction often combines multiple elements:
- Phonics for decoding
- Vocabulary for meaning
- Fluency for smooth reading
- Comprehension strategies for deeper understanding
Phonics acts as the foundation that supports these other skills. Without it, reading development can become uneven or difficult to sustain.
Conclusion
Phonics plays a vital role in reading development by supporting both word decoding and reading comprehension. By teaching the relationship between letters and sounds, phonics helps readers approach text with confidence, accuracy, and understanding.
When decoding becomes automatic, readers are free to focus on meaning, ideas, and enjoyment. This leads to stronger comprehension, better fluency, and a more positive reading experience overall.
Whether for young learners, struggling readers, or adults improving literacy skills, phonics remains a powerful and practical tool. Understanding how phonics works—and why it matters—can help readers at every level unlock the full potential of written language.